 |
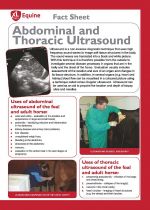
Ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic technique that uses high frequency sound waves to image soft tissue structures in the body. The sound waves are translated into a black and white picture. With this technique it is therefore possible from the outside to investigate several disease processes in organs that are in the belly and the chest of the horse. Evaluation usually includes assessment of the location and size of an organ and changes in its tissue structure. In addition, in several organs (e.g. heart and kidney) blood flow can be visualised in a coloured picture using a technique called colour-Doppler ultrasound. Ultrasound can be used as an aid to pinpoint the location and depth of biopsy sites and needles. |
 |
Acorns are poisonous to horses. This is because they contain toxic substances called Gallic Acid and Tannic Acid.
These acids can cause liver, kidney and intestinal damage to horses eating acorns, oak leaves or branches.
Acorn poisoning is rare but can be a particular problem in the autumn for horses allowed to graze near oak trees. |
 |
Acupuncture involves the insertion of very narrow solid needles into the body with the purpose of modifying disease and providing pain relief.
Acupuncture needles stimulate nerves in skin and muscle and increase the body’s release of natural painkillers - endorphins and serotonin. These chemicals act in the pain pathways of both the brain and spinal cord which can result in exceptional pain relief. |
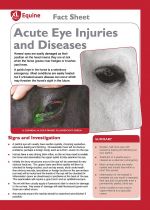 |
Horses' eyes are easily damaged as their position on the head means they are at risk when the horse grazes near hedges or brushes past trees. |
 |
Horses are not usually aggressive; on the whole herds stay together because they form a hierarchy within the group, allowing them to get on well with each other. When a horse shows aggression, it is generally as a result of a perceived threat from either the environment in which it finds itself or in response to a noxious stimulus from within the animal itself, for example an animal in pain. |
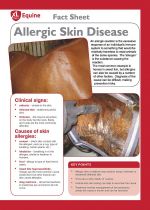 |
An allergic reaction is the excessive response of an individual’s immune system to something that would be relatively harmless to most animals of the same species. The ‘allergen’ is the substance causing the reaction.
The most common example in horses in sweet itch, but allergies can also be caused by a number of other factors. Diagnosis of the cause can be difficult, making prevention tricky. |
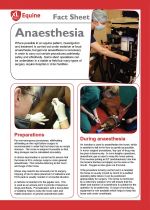 |
Where possible in an equine patient, investigation and treatment is carried out under sedation or local anaesthesia, but general anaesthesia is necessary in order to carry out certain procedures painlessly, safely and effectively. Some short operations can be undertaken in a stable or field but many types of surgery require hospital or clinic facilities. |
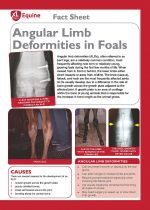 |
Angular limb deformities (ALDs) , often referred to as bent legs, are a relatively common condition, most frequently affecting new born or relatively young, growing foals during the first few months of life. |
 |
Antibiotics are pharmaceutical products which kill or prevent the replication of bacteria. Veterinary surgeons use them in equine practice for the treatment of bacterial disease. Antibiotics are broadly classified into two categories – they are either bacteriostatic, whereby they inhibit bacteria from growing, allowing the animal’s own immune system to deal with them, or bacteriocidal, where the antibiotic itself kills the bacteria. Bacteria can also be classified as either Gram positive or Gram
negative depending on how they appear when stained and examined under a microscope. Different antibiotics are good at targeting different bacteria. Those with the widest range of activity are known as broad spectrum antibiotics. |
 |
Arthritis is a disorder of the joints, characterised by the degeneration and loss of the cartilage covering the joint surface and the development of new bone on joint surfaces and margins. |
 |
Arthroscopy (commonly known as keyhole surgery)
has been available since the 1980s for the treatment of
joint injuries in humans, horses and occasionally dogs.
The procedure allows the examination and treatment
of many joint and tendon canal injuries whilst causing
minimal trauma during the procedure itself. Patients
generally recover relatively quickly following keyhole
surgery with little scarring and low risks of wound
complications. |
 |
Atopy is a hereditary skin disease of dogs, characterised by skin inflammation and itchiness (pruritus). Current understanding is that it is caused by an abnormal reaction of the immune system to tiny particles in the environment called allergens, combined with abnormalities in the surface layer (stratum corneum) of the skin. Allergens enter the body through the skin and lead to the production of certain antibodies in genetically predisposed animals. These antibodies then cause either intermittent or chronic (long-term) symptoms. |
 |
Atypical or sycamore myopathy is an uncommon, sudden onset, severe muscle disease, which is rapidly fatal in about 75% of cases. This disease is seen most commonly in the autumn, in horses and ponies kept at pasture and is associated with the ingestion of sycamore seeds.
It should not be confused with exertional rhabdomyolysis (ERM) commonly known as tying up which is a relatively common muscle condition occurring during or shortly after exercise. |
 |
Exertional Rhabdomyolysis (ERM) is also known as Azoturia,
Tying-up, Set-Fast and Monday Morning Disease. ERM is a disturbance of the normal functioning of the muscles in the horse that causes painful cramps and muscle damage. ERM is most often seen when there is an imbalance between exercise and feeding, for example maintaining a high energy diet while suddenly reducing the exercise levels. In some cases, it is caused by a genetic disease: polysaccharide storage myopathy (PSSM). |
 |
The modern horse we know today has evolved over millions of years, surviving quite happily without human intervention with regards to hoof maintenance. In a natural environment, horses graze varied terrain, wearing away the excess hoof growth to keep the hoof at a constant length without the need for trimming or shoeing.
Horses are now bred for performance and the way in which the modern equine is maintained and managed means that hoof care and maintenance is very important in ensuring soundness and performance. A well balanced foot will be symmetrical in size and shape and land flat on the ground. |
 |
Analysis of blood has long been a standard part of the investigation of a large number of illnesses, diseases and injuries. The number of available tests, along with their accuracy, is continuously expanding, as researchers and laboratories endeavour to make ever greater use of blood testing as a diagnostic tool. The procedure is generally very safe and well-tolerated by most horses and the results can yield important information about the health of a patient. Along with aiding in the diagnosis of disease, blood testing has a number of other uses, as described below. |
 |
Body condition scoring (BCS) is important as it provides an early indication of under or over nourished donkeys.
Condition scoring in the donkey is different to their close relatives, the horse, because fat is stored in different locations on the body.
Visual appearance can be deceptive and therefore a more hands-on approach is required, it is also important to be aware that woolly coats can mask the true BCS. |
 |
Bog spavin is fluid distension of the high mobility joint in the hock called the tibiotarsal or tarsocrural joint. The swelling can be seen and felt at the two superficial outpouchings of the joint capsule; at the front towards the inside and on the outside just below and infront of the point of hock. If one swelling is compressed this usually causes the other swelling to enlarge temporarily and vice versa.
Bog spavin can occur in one or both hind legs. |
 |
Bone spavin is the term used for osteoarthritis of the lower joints within the hock, most commonly the distal intertarsal and tarsometatarsal joints. These joints are all low movement joints unlike the upper joint about which the vast majority of flexion and extension of the hock occurs.
Bone spavin is one of the most common forms of hind limb lameness seen in the horse. It is most frequently seen in mature performance and pleasure horses but can also be seen in young racehorses. It is thought to be caused by repeated compression and rotation of the small bones within the hock; although in some breeds e.g. Icelandic there may also be a hereditary component. Horses with poor hock conformation e.g. sickle or cow hocks are more prone to develop the condition. |
 |
Coccidia are single celled protozoal organisms of the genus Eimeria. They have a complex life cycle involving both asexual and sexual reproduction. |
 |
Bovine Digital Dermatitis (BDD) is a common cause of infectious lameness worldwide. |
 |
It takes four to six months for the eggs in a cow's ovaries to grow to their ovulatory state. Management of the cow during this period is critical in determining their ability to yield transferable embryos that become established pregnancies. |
 |
Before pasteurisation of milk (1935) and compulsory testing
(1950) bovine TB (bTB) was a recognised cause of death in humans.
In cattle, emaciation due to lung disease was common. The testing
programme reduced the incidence of disease in cattle to very low
levels by the late 1970s, but there remained a persistent level of
disease in the South West. |
 |
A bruised sole is one of the most common causes of lameness in horses.
Direct trauma or injury to the underside of the foot can result in haemorrhage and inflammation beneath the sole, involving the sensitive horn producing tissues, leading to the typical dark red appearance of a bruise.
A bruised sole may be caused by accidental injury to the sole of the foot by treading on a stone or un-even ground, pressure from poorly fitting shoes or excessive work on hard ground. |
 |
Managing reproduction effectively to achieve optimum fertility is essential to the running of a profitable cattle enterprise. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about the BVD Virus. |
 |
This leaflet is designed to help you understand what happens if your cat or dog needs to have a caesarean and how to care for them afterwards. |
 |
Respiratory disease in calves is an interaction between the environment, the immunity of the calf and the various infectious agents involved. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about the Calf Scour. |
 |
Campylobacter foetus venerealis is one of the many potential causes of bovine infertility and abortions. It is transmitted from cow to bull to cow at serving. |
 |
Cancer is a term used to describe a condition where
abnormal cells divide without control. As in human
medicine it is hard to say in most cases what has
caused the cancer. Some possible causes include
toxins and chemicals in the environment, faulty
genes, infectious diseases or abnormalities in the
animal’s immune system. |
 |
This ia a condition that affects the frog of the foot. It used to be seen primarily in heavy horses, but we now see it in all breeds. |
 |
The pregnant mare needs special managemnet considerations in order to optimise the chance of the successful delivery of a healthy foal. |
 |
The life span of our horses is increasing:
- approximately 29% of the UK horse population are older than 15 years of age;
- many older horses continue to have a useful working life and still participate in regular athletic activity;
- a recent study showed that older horses received less preventive health care measures, such as vaccination, farriery and routine veterinary care, when in fact they often need an increased level of care in these areas. |
 |
Choke is a relatively common condition seen in horses and ponies and is typically caused by obstruction of the oesophagus (food pipe) with food; occasionally a foreign body can be involved e.g. wood or plastic. Fortunately many cases of choke resolve quickly and spontaneously and only cases in which the obstruction lasts for longer than 30 minutes are likely to require veterinary assistance.
It is important to note that this is not the same as the life-threatening condition in humans, where the term “choke” refers to blockage of the windpipe rather than the oesophagus. This difference means that unlike humans, horses with choke can still breathe. |
 |
Chronic renal disease is a common disease of older
cats, but may also occur in young cats and dogs. It
is often caused by ongoing damage to the kidneys
over time, however injuries, toxins, infections, cysts
or tumours can also cause kidney disease.
Until the disease is relatively advanced it may be
difficult to detect, and by the stage at which signs
of illness are obvious, only 25% of normal kidney
function may remain. |
 |
Colic simply means 'pain in the abdomen' and therefore has many different causes. It may be serious or even life-threatening, but most horses with colic recover fully and uneventfully. |
 |
Colostrum is the fuel of life and making sure your calves get enough is the cornerstone to all successful calf rearing enterprises. |
 |
A corn is a bruise that forms between the sensitive and insensitive layers of the sole of the foot. |
 |
Cryptosporidiosis is a disease caused by Cryptosporidium parvum (C. parvum)infection which is spread by contact with reservoir hosts, i.e. cattle, sheep and goats or the environment in which these are housed. |
 |
Pets with this condition produce excessive amounts
of hormones, especially cortisol, from the adrenal
glands. It is usually the result of a tumour (most
commonly benign) either in the pituitary gland at
the base of the brain or in the adrenal glands. The
adrenal glands are found in the abdomen close to the
kidneys. |
 |
Equine Cushing’s is now termed PPID (Pars Pituitary Intermedia Dysfunction). This means that an area of the pituitary gland at the base of the brain overproduces several hormones. This results in raised ACTH1 which circulates in the blood to the adrenal glands and causes excess cortisol (a steroid hormone) to be produced.
It is a gradual age-related change so primarily affects ponies and horses over 15 years of age but recent studies have shown it to be evident in some 10-15 year olds.
A significant proportion of horses with laminitis have PPID. |
 |
This factsheet looks at Dairy Cow Lameness. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about Dairy Herd Biosecurity. |
 |
When an infectious disease such as 'Strangles' is suspected; people often
hope there is a less serious cause and carry on as normal to avoid any
associated panic. If you are unlucky enough to have an infectious disease,
ignoring the problem in the early stages will only increase the number of
horses affected and prolong the length of time the yard is affected. |
 |
Dental disease is one of the most common problems
in cats and dogs. It can be the cause of bad breath,
bleeding gums and chronic pain but can also be a
source of infection which can spread to other parts of
the body including kidneys, liver and the heart. |
 |
Diabetes is a problem that can affect both dogs
and cats. It is a condition where there is a higher
than normal level of glucose (sugar) in the
blood and urine. This leaflet will explain how the
disease can be identified and what can be done to
manage it. |
 |
Diarrhoea is an increase in the volume, fluidity and frequency of droppings and can vary in severity from mild to severe. The horse’s large intestine (colon), acts as a fermenting vat containing numerous bacteria and large volumes of fluid for the digestion of fibrous feeds. In most cases of diarrhoea there is disruption of the normal bacterial population in the gut which can impair digestion. In severe cases of diarrhoea the fluid losses can be rapid, leading to marked dehydration and electrolyte losses. Without prompt veterinary treatment diarrhoea can be a life threatening condition. |
 |
With increasing movement of horses worldwide and climate warming, diseases which are common in tropical and subtropical countries can be found travelling north; demonstrated by the recent outbreaks of Bluetongue and Schmallenberg disease in the British farm population. The threat of a devastating disease like African horse sickness entering the UK and killing a large proportion of the horse population is so real that the government has already put regulations in place for managing a possible outbreak. The risk of the entry of a new equine disease into the UK has the potential to not only cause welfare issues and equine deaths but the possibility of large scale disruption of equine events and activities of the scale seen in the foot and mouth outbreak of 2001.
Horse owners and veterinarians should be vigilant and keep exotic diseases in their mind when dealing with a sick animal or sudden unexplained death. It is imperative that these situations are recognised in the earliest possible stage and appropriate biosecurity measures are put into place to minimise spread. |
 |
Castration of donkeys requires special care because donkeys have a larger blood supply to the testicles compared with horses and as such are at greater risk of bleeding post-surgery.
For this reason most donkey castrations are performed under general anaesthesia (GA), to allow a ligature (secure suture) to be placed around the blood vessels. This reduces the risk of post-operative bleeding and intestinal prolapse through the surgical incision. Due to the need for GA and the technique required, castration is best performed at the clinic. |
 |
The term ‘colic’ describes the symptoms displayed when a horse or donkey is suffering from abdominal pain. Donkeys are very stoical by nature and therefore rarely display the same clinical signs as horses; instead they tend to present as dull and off their feed. Monitoring a donkey’s demeanour and normal bowel habits can be helpful in identifying those affected before the condition deteriorates.
The causes of colic in donkeys are very varied and commonly include blockage with partially digested food material (impaction), muscle cramps of bowel wall (spasmodic) or a build of gas within the bowel. Investigation of colic is aimed at identifying the patient’s physical status and the cause of the colic so that medical or surgical treatment can be tailored accordingly. |
 |
Donkeys (and small pony breeds) are at particularly high risk of developing hyperlipaemia - abnormally high levels of triglycerides (fat) circulating within the blood. This occurs when the body’s energy supplies are limited (e.g. off feed) or nutritional demands are increased (e.g. pregnancy, disease) coupled with a metabolic abnormality called insulin resistance (donkeys are inherently insulin resistant). Hyperlipaemia can be a primary condition or secondary to anything which causes a donkey to go off its food.
Hyperlipaemia is associated with a high mortality (death) rate due to organ failure and therefore recognition of ‘at risk’ animals is essential. Prompt and aggressive intensive care treatment of affected animals is essential to optimise their chances of survival. |
 |
Donkeys have evolved to live in arid, mountainous, desert areas where feed is sparse and of poor quality. As a consequence, they are excellent at digesting very fibrous plants and can feed off woody shrubs and trees as well as grass. Replication of this natural environment can be very difficult in the UK where donkeys are commonly kept as companion or leisure animals on lush, grass-rich pastures.
Every donkey should be fed according to their body condition, age, underlying health issues, time of year and grazing availability. Inappropriate feeding can lead to boredom, obesity and the potentially serious health issues that occur as a consequence of this. |
 |
Donkeys are not small horses, and their natural environment is not the temperate conditions of the UK but a more semi-desert like environment where food is scarce and of a poorer quality.
In the UK donkeys live a pasture lifestyle, and many of the clinical problems which arise are the result of too much food and not enough exercise. These are problems which are exacerbated as a donkey reaches old age.
Donkeys frequently live into their thirties, so are a long term undertaking and need regular veterinary and dental care throughout their lives. |
 |
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS) is a relatively
common problem seen in dogs, often termed ‘dry
eye’. Dry eye occurs due to a reduction in the quality
of tear production in your dog’s eye. Tears normally
keep your pet’s eye healthy and lubricated. If your
pet is not producing enough tears they can quickly
develop sore, infected eyes and in severe cases
vision can be affected. |
 |
Endoscopes are instruments which can be used to look inside a horse’s body. They are long, tubular, and generally flexible. They have a light and a camera at their far end. The tip is manipulated by dials on a hand piece. Your vet will be able to view the image either through an eyepiece, or on a computer screen.
Endoscopes have many uses in equine practice, but the most common endoscopes are between one and 1.5 metres in length and are used to view the horse’s respiratory tract. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about Environmental Mastitis. |
 |
Epilepsy is the term vets use if your pet is having
repeated fits or seizures.
For many pets no specific cause of the fits can be
found. Vets call this “primary” or “idiopathic” epilepsy.
These patients appear normal between fits.
Fits can be caused by a problem elsewhere in your
pet’s body. Vets call this “secondary” epilepsy. These
patients may show other problems between fits. |
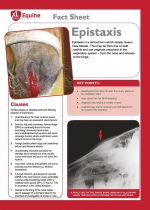 |
Epistaxis is a clinical term which simply means nose bleeds. This may be from one or both nostrils and can originate anywhere in the respiratory system – from the nose and sinuses to the lungs. |
 |
Most mares that conceive remain healthy throughout pregnancy and foal normally when expected, but, unfortunately, a few mares will lose their foal either early or late in pregnancy. Early embryonic loss occurs relatively commonly in the first couple of months of pregnancy, usually because the embryo is not developing correctly or the uterus (womb) is not as healthy as it should be. Older foetuses may be aborted by the mare for a number of reasons (see causes). If the foetus is less than five months of age, it may be fully resorbed by the uterus so there is no external evidence of this miscarriage. Over five months of age, the foal will be expelled by the mare, along with the placenta and associated fluids. If this occurs outside, it may go unnoticed, as it can be a relatively ‘clean’ process and the foetus may be removed by wildlife. |
 |
All horses should receive routine dental care at least once a year to prevent sharp enamel points forming which can cause trauma to the soft tissues of the mouth. |
 |
Dentistry is an essential and important part of the health care of your horse. Your horse's teeth should be examined at least once a year. |
 |
There are three main types of herpes virus in horses:
Equine herpesvirus 1 (EHV-1); which causes respiratory disease and also occasionally abortions and neurological disease.
Equine herpesvirus 4 (EHV-4); causes respiratory disease (generally mild).
Equine herpesvirus 3 (EHV-3); which is less commonly seen but may cause venereal disease in breeding mares and stallions. |
 |
Equine Infectious Anaemia (EIA) also called
'swamp fever' is a viral disease transmitted from
infected to non-infected horses by biting flies
e.g. horse flies and via infected blood and blood
products including contaminated needles and
syringes.
The disease is not currently in the UK but is
circulating in Europe in particular Italy and
Romania. There was a significant outbreak of
EIA in Ireland in 2006 following the introduction
of the virus in imported blood products. More
recently in England in 2010 and 2012 cases
were identified in horses that had been
imported previously. |
 |
LASER is the acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation.
A laser generates an intense beam of light that for surgical purposes can be used to cut, seal or vaporise tissue. There are three different types of laser used: CO2, diode and Nd:YAG.
The CO2 laser heats up water within the tissue and vaporises it. This laser has the advantages of sparing surrounding tissue from heat damage and precise cutting capability.
Both diode and Nd:YAG deliver the laser down a fibre allowing it to be passed down a video-endoscope and used for endoscopic guided surgery. The laser energy is more easily absorbed by tissue than CO2 laser, resulting in increased risk of heat damage to tissue. The diode laser is becoming increasingly popular in large animal practice as it is small, portable and efficient. |
 |
Equine Metabolic Syndrome (EMS) is a condition which has only become recognised in recent years. EMS is usually seen in overweight horses and ponies. Fat which is laid down around the body becomes hormonally active and excretes hormone-like chemicals which interfere with normal sugar and fat metabolism. The result is an individual that continues to put on weight and will, eventually, show signs of laminitis. It has similarities to Type 2 diabetes in humans.
EMS in natural living, wild, native ponies is normal. It allows them to put on weight in the summer and then use these fat reserves in the winter months when food is in shorter supply. Our domestication of horse and ponies – rugging up and liberal feeding all year round – interferes with this natural mechanism. |
 |
Broadly speaking, muscle diseases (myopathies) are either present from birth (genetic disorders) or develop spontaneously during adulthood (acquired disorders). Those present from birth may not be obvious until adulthood.
The medical term for the most common muscular disorder is recurrent exertional rhabdomyolysis (RER), resulting in a syndrome of muscle cramping that occurs during exercise. RER is also known as tying up, setfast, Monday morning disease and azoturia. Horses that experience RER either have an underlying myopathy or have been physically overexerted. |
 |
Equine Viral Arteritis (EVA) is caused by equine arteritis virus. The virus occurs worldwide. Infection can be transmitted between horses during mating or teasing, via infected semen used in artificial insemination, by contact with aborted foetuses or placentas or via the respiratory route. |
 |
Euthanasia is one of the most difficult times we face as pet owners. Knowing how to make it at the ”right” time troubles many owners and this leaflet aims to help that decision-making for you. |
 |
The decision to euthanase a horse may be the most
difficult faced by an owner.
In addition to the emotional stress, the situation is further complicated by the practical arrangements necessary. While the decision can never be made easy, considering the options available in
advance can help to prevent further distress both during, and after the procedure.
It can be useful to leave a plan of your arrangements with your yard owner or temporary carer, so that if you are unavailable in an emergency situation, your wishes can still be respected. |
 |
Your ram is half the solution to getting a high percentage of ewes in lamb quickly to give a tight lambing period and help get lambs away early. He may also have cost a lot of money in the hope of
either improving the genetics of the flock or producing better lambs for sale. However, too often his ability to mate ewes and get them in lamb is taken for granted, often until it is too late and ewes are returning. A pre-breeding exam can rule out common problems and may indicate the need for collecting and testing a sample of semen to confirm fertility. |
 |
FLUTD is a term used to describe a collection of
conditions relating to the bladder and urethra in cats.
There can be many contributing factors including
bladder stones, anatomical defects, bacterial
infections and behavioural problems. In most cases
however it is not possible to identify an underlying
cause so the problem is referred to as being idiopathic. |
 |
First aid as the name suggests is the first treatment
you would give when presented with an injury or
traumatic episode. We all hope that our pets will
never be in the situation where it is needed however
the preparation of a basic first aid kit and some tips
on how to handle situations may make dealing with
an emergency much easier. |
 |
Wounds are very common injuries in equines and it is vital for the horse owner to be able to evaluate the severity of a cut. Some wounds can be managed without veterinary assistance but many will require professional attention. It may be possible to provide important first aid before the vet arrives.
Innocuous-looking wounds can be the most dangerous, so if you are in any doubt as to the significance of a wound it is best to contact your vet for advice. |
 |
Fleas are a very common problem for many pet owners that can exist all year round and in some animals can be the cause of unpleasant skin conditions. This leaflet will help you understand how to identify fleas, how to treat them and how to prevent them becoming a problem in your home. |
 |
Also known as pus in the foot, this condition is very commonly seen in horses, ponies and donkeys. Foot abscesses are generally very painful with a sudden onset. They result from a localised bacterial infection developing inside the hoof wall or under the sole, which typically develops after a penetrating injury through the sole, or by tracking up the white line (the seam between the sole and the hoof wall). Recurrent abscesses at the same location can reflect either the presence of a deep seated unresolved infection, a foot tumour called a keratoma, infection of the pedal bone within the foot or chronic laminitis. |
 |
With many new born animals, for example dairy calves, it would be common for them to be bucket reared on artificial milk powder. Orphan foals however benefit hugely from being reared by a foster mare, both in terms of behaviour and social development, as well as meeting their nutritional needs.
In the early weeks of life foals feed very frequently and bucket, or bottle rearing a foal is very time consuming. In contrast, fostered foals can live a more normal life with their new mother; they benefit from feeding when they need to and being able to be turned out as part of a herd. |
 |
Fractures can occur as a result of stress due to repeated forces exerted over time, or from an immediate impact which can occur with a kick or a fall. |
 |
Equine gastric ulcer syndrome (EGUS) describes the erosion of the horse’s stomach lining due to prolonged or excessive exposure to acid produced by the stomach. Any horse can suffer from gastric ulceration, from elite performance horses to pleasure horses and ponies. |
 |
Gastroenteritis, or sickness and diarrhoea, is a
very common problem in cats and dogs.
It is usually mild but in severe cases can become
life threatening. This leaflet will help you understand
how to manage the problem and when to contact
the vet for help. |
 |
Equine grass sickness (EGS) has been recognised in this country since the early 1900’s. It is found in countries around the world but is most common in the UK. It does not affect humans and is not contagious i.e. it is not passed from horse to horse.
Disease occurrence around the UK varies, being more common in the drier eastern counties and in Scotland. The incidence peaks in the spring and early summer. There are three forms of EGS: Acute, Sub-acute and Chronic. All are very serious and usually fatal. Occasionally, with good nursing and specialist care, chronic cases can recover. |
 |
Headshaking sounds such an innocuous term but it can make the affected horse’s life a misery and render them un-rideable.
Horses may shake their heads for a variety of reasons: for example due to pain in the mouth or back. In some, it may be a response to stress or in anticipation of food or exercise. All of these are voluntary actions; the horse is choosing to toss his head. Headshaking syndrome is different, it is an involuntary action thought to be caused by pain in a nerve supplying the face. |
 |
It is estimated that heart problems can affect up to 10% of dogs and cats in the UK. Some heart diseases may be present when the animal is born, however the majority develop in adulthood. This leaflet will help you understand what can happen if your pet has a heart problem, how the condition can be diagnosed and how it can be treated. |
 |
A heart murmur is a sound produced in the heart by the turbulent flow of blood. Due to the large size of the horse’s heart, this turbulence can be normal (physiological or flow murmurs) e.g. from a fast flowing large volume of blood, or from a high blood flow rate during exercise or in cases of anaemia. Murmurs also result from abnormal blood flow through the heart e.g. back flow through a leaking valve or flow through a hole in the heart. |
 |
Hoof cracks can occur in all breeds of horses and ponies and can be a significant cause of foot problems and lameness. Once formed, the cracks can take many months to grow out and in severe cases can cause recurrent problems.
Recognising when your horse has a crack and getting suitable, prompt treatment, can help to significantly reduce the time and interventions needed to enable a crack to heal. |
 |
All horses, ponies, donkeys, zebras and their crosses must have an equine passport. The only exceptions are listed wild and semi wild ponies in designated areas of Dartmoor, Exmoor and the New Forest. |
 |
Hyperthyroidism is a condition frequently seen in middle aged and older cats. It is caused by an excessive production of thyroid hormones from the thyroid gland in the neck (or occasionally thyroid tissue found elsewhere in the body). Thyroid hormone regulates the metabolism so an overproduction of hormone increases metabolic rate and can have effects on all the body’s major organ systems |
 |
IBR is the most obvious clinical disease associated with infection by Bovine Herpesvirus 1 (BoHV-1). IBR is a disease of the upper respiratory tract which varies in severity, depending on the strain
of virus involved and other factors which may influence the immune status of the animal. In severe
cases, damage to the upper airways may lead to pneumonia and sometimes death. BoHV-1 infection has also been associated with infertility, abortion, high temperatures and milk drop. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about infertility problems in dairy herds. |
 |
Recurrent airway obstruction (RAO) is a common cause of coughing, nasal discharge and poor performance in many stabled horses. Whilst several therapies exist, the use of inhaled drugs plays an important role in the long term treatment of affected horses. |
 |
Insurance is a vital part of responsible horse ownership. Not only can it provide cover for vet’s fees in case your horse becomes ill or injured, but it can also cover against third party liability, loss of use, mortality and personal accident.
As with car insurance, there are numerous insurance companies providing cover for you and your horse. There are also different levels of cover, from the companion animal to international eventers and show-jumpers, covering all different types and levels of athletic ability. |
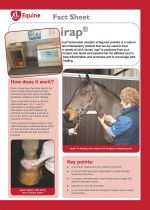 |
irap® (interleukin receptor antagonist protein) is a natural anti-inflammatory product that can be used to treat a variety of joint injuries. irap® is produced from your horse’s own blood and injected into the affected joint to treat inflammation and lameness and to encourage joint healing. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about Johne's Disease. |
 |
Over the past two decades, joint supplements have been increasingly used in an attempt to both treat and prevent joint injury and degeneration. There is now an extensive range of products available for use as a daily in feed supplement.
There is a lack of good evidence regarding their efficacy; that may be due in part to the large variations between the concentration, and quality, of the ingredients between products.
It appears that joint supplements may benefit some patients but not others. |
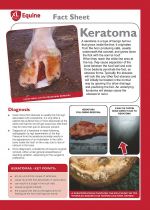 |
A Keratoma is a type of bengin tumor that grows inside the foot. It orginates from the horn producing cells, usually underneath the coronet, and grows down the foot with the normal hoof. |
 |
Laminitis, in its simplest form, is inflammation of the sensitive layers (laminae) of the hoof resulting in pain, inflammation and, in some cases, permanent damage to the laminae. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about liver fluke in cattle. |
 |
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) is an imaging technique that involves placing the horse within a strong magnetic field. Radio waves are applied to the area to be examined and the signal produced is analysed by a computer to produce an image. The high tissue contrast achieved allows assessment of cartilage, ligament, tendons, joint capsule and bone; all on one image. MRI can image deep inside structures and in three dimensions so changes can be found that may not be seen using other imaging e.g. x-ray. MRI is most commonly used for lameness investigations. |
 |
A phobia is defined as an extreme fear or aversion
to something. In pets the most common phobias
are associated with loud or sudden noises such as
thunder, fireworks and gunshots. |
 |
The time immediately around calving (periparturient period) is the most critical part of a cow's year for many health and production reasons. |
 |
Perhaps the most common and significant neurological disorder, metabolic disease tends to affect adult sheep, particularly around lambing time. |
 |
Microchipping is an important part of responsible pet ownership and provides peace of mind that that if your pet was to go missing, he or she would have the best chance of being returned home safe and sound. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about Milk Fever. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about how you can minimise calving difficulties. |
 |
Nail bind is a term used to descibe the condition where a nail has been driven too close to the sensitive laminae in the horse's foot. |
 |
Advances in reproductive technology over the past decade have greatly improved Artificial Insemination (AI) pregnancy rates. It is now practised widely throughout the UK in many different breeds, the most notable exception being the racing Thoroughbred (TB). Natural service remains the best option in some situations, though, depending on the type of mare, and has proved successful since Eohippus roamed the earth 50 million years ago! |
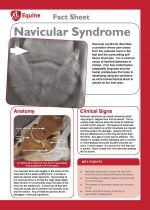 |
Navicular syndrome describes a condition where pain arises from the navicular bone in the foot and the surrounding soft tissue structures. It is a common cause of forelimb lameness in horses. Poor foot conformation (especially long toes and low heels) predisposes the horse to developing navicular syndrome as extra biomechanical strain is placed on the heel area. |
 |
Lameness accounts for a large proportion of any equine vet’s caseload. The actual cause of lameness may be determined following physical examination if there is an obvious swelling or area of pain, but often further investigation is necessary to localise the problem and identify the cause. Orthopaedic investigations often involve the use of nerve and joint blocks.
Nerve blocks refer to the injection of local anaesthetic around the nerves in your horse’s limb. These differ from joint blocks where the local anaesthetic is injected directly into a joint or tendon canal. |
 |
The majority of bitches in the UK will be spayed (neutered) at some point in their lifetime. However, deciding whether this is appropriate for your bitch and what is the best time for the surgery are things that should be discussed with your vet. This leaflet will help you understand the procedure and its benefits. |
 |
Castration is a common surgical procedure performed on male dogs. The decision whether or not to castrate should be taken after discussion with your vet. This leaflet will give you more information and may help you decide what questions you should ask about the procedure. |
 |
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are probably some of the most widely used drugs used in both human and equine medicine. They act to reduce pain by inhibiting the inflammatory pathways after injury. Common NSAIDs used in human medicine include aspirin, paracetamol and ibuprofen. NSAIDs used in equine medicine include phenylbutazone (bute), meloxicam, suxibuzone and flunixin. |
 |
There has been a lot of media attention regarding human obesity and it is no surprise that being overweight is not good for horses or ponies either. Overweight horses are seen far too often and despite efforts being made in the showing world by judges and exhibitors, it continues to be a big problem throughout the horse population in this country. Obesity in horses and ponies can be a serious welfare problem; there is a greatly increased risk of equine metabolic syndrome (EMS) which commonly leads to laminitis. |
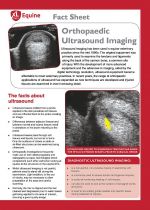 |
Ultrasound imaging has been used in equine veterinary practice since the mid 1980s. |
 |
Osteoarthritis is a debilitating, painful condition
affecting the joints, in which there is progressive
destruction of cartilage and degeneration of all
joint tissues. Arthritis cannot be cured, but it can be
managed very successfully |
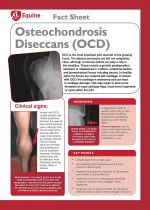 |
OCD is the most important joint disorder of the growing horse. The disease processes are still not completely clear, although numerous factors can play a role in the condition. These include a genetic predisposition, excesses or imbalances in nutrition, endocrine factors and biomechanical forces including trauma. In healthy joints the bones are covered with cartilage. In horses with OCD this cartilage is weakened and can lead to cartilage damage. This may repair or lead to the formation of loose cartilage flaps, loose bone fragments or cysts within the joint. |
 |
Horses are most commonly vaccinated against influenza and tetanus (see 'Vaccinations against influenza and tetanus' factsheet.) This fact sheet concentrates on other vaccinations of the horse, namely; equine herpesvirus (EHV), equine rotavirus, equine viral arteritis (EVA) and strangles. |
 |
Abortion in sheep is common, but it should not be thought of as inevitable. There are excellent vaccines for the commonest causes of abortion and some of the other causes have factors that can be reduced. |
 |
The pancreas is an organ involved in digestion.
It produces enzymes which help to digest food
and neutralise stomach acid. Pancreatitis occurs
when the pancreas becomes inflamed. When
inflammation occurs, the digestive enzymes
are released into the pancreas and surrounding
tissues rather than being released into the guts.
This causes severe pain as these enzymes start
to digest the pancreas. |
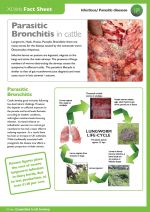 |
Lungworm, Husk, Hoose, Parasitic Bronchitis: there are many names for the disease caused by the nematode worm Dictyocaulus viviparous.
Infective larvae on pasture are ingested, migrate to the lungs and enter the main airways. The presence of large numbers of worms obstructing the airways causes the symptoms in affected cattle. The parasite’s lifecycle is similar to that of gut roundworms and most cases occur in late summer / autumn. |
 |
Pastern dermatitis means inflammation of the skin of the pastern between the fetlock and the hoof. It is a description of a clinical appearance rather than a specific diagnosis. There are a large number of causes of pastern dermatitis. Effective treatment will depend on accurate diagnosis of the inciting factors, although this can be difficult as the skin inflammation may look fairly similar irrespective of the cause. |
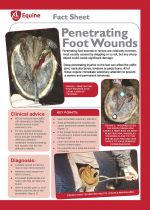 |
Penetrating foot wounds in horses are relativley common, most usually caused by stepping on a nail, but any sharp object could cause significant damage. |
 |
In recent years veterinary medicine has become increasingly more sophisticated. We are able to diagnose and treat conditions that a few years ago would have remained undetected. The downside of these advances is an increase in the associated costs. This leaflet is designed to help you understand pet insurance, how to select the policy that is right for you and where it can help. |
 |
After an injury or illness physiotherapy can be used to optimise the conditions for healing, promote mobility and restore function.
Current legislation only permits the use of ‘physiotherapy’ (including chiropractic and osteopathy) under the direction of a registered veterinary surgeon i.e. by referral. Physiotherapy is a science based profession that is assessment driven and thus requires regular reviews. |
 |
Platelet Rich Plasma or PRP is a concentrated solution of a horse’s own platelets. Platelets are a type of cell found in the circulation involved in blood clot formation and healing. When injected into damaged tissues, these platelets will release growth factors, which are involved in the healing process. They encourage tissues to re-generate and new blood vessels to grow, which in turn bring oxygen and nutrients to the damaged tissue. It is thought that by this process the body’s own natural healing is magnified to achieve better quality tissue repair, giving a better prognosis for future soundness. |
 |
Cruciate ligaments are important structures within the knee joint necessary for joint stability and normal function. Ligament rupture causes knee joint pain and instability which can in turn lead to development of other painful problems such as meniscal (cartilage) damage and arthritis. |
 |
Cruciate ligaments are important structures within the knee joint necessary for joint stability and normal function. Ligament rupture causes knee joint pain and instability which can in turn lead to development of other painful problems such as meniscal (cartilage) damage and arthritis. |
 |
Breeding your own foal from a beloved mare can be immensely rewarding, but remember it is a long term project requiring a lot of commitmnet in terms of time, energy and money. |
 |
Biosecurity is a set of management practices that reduces the potential for the introduction or spread of disease-causing agents. Setting up a yard plan and maintaining good biosecurity practices will:
- help prevent the introduction and spread of contagious diseases such as equine influenza
and Strangles;
- assist in keeping the horses healthy and performing well;
- help prevent unnecessary disruption to equine activities and the operation of an equine business and the considerable associated costs. |
 |
Psyllium fibre is a digestive supplement for horses. Made from psyllium seed husks, it absorbs water in the intestine, forming a gel like substance which picks up sand and dirt. For this reason it is often given to horses after an episode of sand colic. |
 |
Rabbits are the third most popular British pet; here are some pointers that XLVets recommend to help keep your rabbit fit and healthy! |
 |
Ragwort is a very common plant with yellow flowers. It is often seen growing on rough land and on the roadside verges. |
 |
Rain scald is a condition generally during autumn and winter months and affects the skin of the horse, usually on the back and the flanks. |
 |
Recurrent airway obstruction (RAO) is an environmentally induced, non-infectious, non-contagious, inflammatory airway disease of horses. |
 |
Mechanically the foot has three main functions; shock absorption, support and grip when the limb is bearing weight. It also provides propulsion when the limb leaves the ground.
The effects of abnormal conformation or inappropriate foot trimming and farriery can lead to uneven loading, poor biomechanics, resulting in an increased risk of injury to structures in the foot and higher up the limb. |
 |
Ultrasound imaging has been commonly used to assist with equine reproduction for over thirty years. Advances in technology and image quality have meant that high quality, portable imaging is affordable to most veterinary practices. Ultrasound is relatively non-invasive and can be performed in many horses without sedation especially where stocks are available to provide restraint. It is most commonly used for assessing the reproductive tract prior to breeding or in mares with behavioural problems and for the detection and monitoring of the progress of pregnancy. |
 |
Ringworm is a highly contagious fungal infection of the skin. It is spread either directly from horse to horse by contact, or indirectly via tack, grooming aids, infected rugs or clothing. Other species in particular cattle can also be a source of infection. Good hygiene is essential to control the spread of infection. The spores can survive in the environment so once one case is seen on a yard other cases often appear. The incubation period is 4-30 days so by the time a horse shows symptoms the disease may have spread to other horses on the yard. |
 |
Castration involves the surgical removal of both testicles. This is carried out to prevent unwanted breeding and behaviour associated with some stallions. |
 |
Equine sarcoids are spontaneous, locally invasive tumours of the skin of horses, mules, and donkeys affecting all breeds, ages, colours and sexes and are the most commonly encountered of all the equine tumours. They are variable in appearance, location and rate of growth and although they seldom affect a horse’s usefulness unless they are in a position likely to be abraded by tack. They are however unsightly and may cause considerable discomfort to the horse. They are commonly seen in moist areas of skin such as the groin, chest, neck and face and particularly in younger animals (one-six years old) and geldings; they are frequently associated with wound sites and often multiply. Transfer and spread by flies has been implicated. Familial tendencies have been identified and a genetic susceptibility has been suggested. |
 |
Schmallenberg virus was first detected in August 2011 within Germany, spreading to the Netherlands, Belgium and now the UK. |
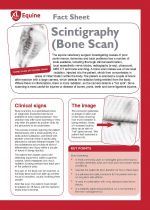 |
The equine veterinary surgeon investigating causes of poor
performance, lameness and back problems has a number of
tools available, including thorough clinical examination,
local anaesthetic nerve blocks, radiography (x-ray), ultrasound,
MRI, CT and bone scanning. A bone scan makes use of low level
radiation, injected into the patient, which then concentrates in
areas of inflammation within the body. The patient is scanned a couple of hours after injection with a large camera, which detects the radiation being emitted from the body. Where there is inflammation, there is more radiation, so the camera detects a “hot spot”. Bone scanning is most useful for injuries or disease of bones, joints, teeth and some ligament injuries. |
 |
The sheath of a gelding or stallion protects the penis when it is not extruded for urination or breeding. |
 |
For many UK fl ocks, lameness is an endemic problem and prevalence has probably increased following the change in weather patterns to mild winters and wet summers. |
 |
Extra-corporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) provides a non-invasive approach to the treatment of musculoskeletal disorders in the horse. Shockwaves are energy-laden sound waves which are directed at the affected area and trigger the body’s own repair and healing mechanisms. |
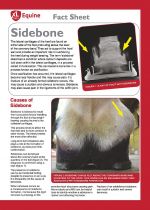 |
The term 'sidebone' describes a condition where calcium deposits are laid down within the lateral cartilages, in a process called mineralisation. |
 |
Steroids are a type of pharmaceutical that can be divided in two general categories. The first are called corticosteroids, which are potent anti-inflammatories used for a range of conditions from lameness to intestinal and respiratory problems. The second include anabolic steroids which are used to stimulate muscle development and general weight gain. This factsheet covers the use of corticosteroids, which are similar synthetic versions of a natural hormone produced by the adrenal glands, next to the kidneys. |
 |
Strangles is a very common but unpleasant bacterial disease that can affect horses, ponies and even donkeys. Signs vary between individuals and can range from very mild to dramatic in appearance. The disease is caused by bacteria called Streptococcus equi subspecies equi (Strep. equi) and is highly contagious being spread by direct contact with infected discharges or with contaminated clothing or equipment. Horses can be silent carriers of the bacteria displaying no outward signs but being capable of infecting others. |
 |
British summer weather may be unpredictable but summer mastitis certainly isn't. It is a disease that changes little over the years, affecting the same farms year after year and often just certain fields within those holdings. |
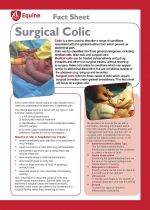 |
Colic is a term used to describe a range of conditions associated with the gastrointestinal tract which present as abdominal pain.
Colic can be classified into three general categories, including:
Medical colic, false colic and surgical colic.
Medical colic can be treated conservatively using drug therapies and other non-surgical means, without resorting to surgery. False colic refers to conditions which can appear similar to abdominal discomfort, but are conditions outside of the abdomen (e.g. tying up and laminitis).
Surgical colic refers to those cases of colic which require surgical correction under general anaesthesia. This fact sheet will focus on surgical colic. |
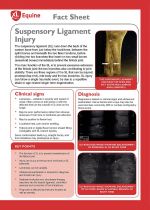 |
The suspensory ligament (SL) runs down the back of the cannon bone from just below the hock/knee, between the splint bones and beneath the two flexor tendons, before dividing into two branches that insert on two small bones (sesamoid bones) immediately behind the fetlock joint.
The main function of the SL is to prevent excessive extension of the fetlock joint; the two branches also contributing to joint stability. There are three regions of the SL that can be injured; proximal (top end), mid-body and the two branches. SL injury can follow a single traumatic event, be due to a repetitive strain or age related longer term degeneration. |
 |
Sweet itch is a hypersensitivity reaction to the bite of a midge which produces skin irritation that leads to rubbing, scartching and biting of the affected areas resulting in hair loss and skin damage. |
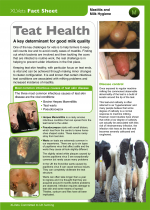 |
This factsheet provides details about teat health. |
 |
Flexor tendon injuries are relatively common in horses. Superficial digital flexor tendon (SDFT) injuries are particularly common in eventers and racehorses, but can occur in any horse through field injury or over-exertion. The primary defect is a central rupture of tendon fibres resulting in bleeding and swelling. A tendon injury need not be career ending as most are treatable, but prompt diagnosis and early, appropriate treatment can prevent catastrophic breakdown and reduce the risk of recurrence. |
 |
Tetanus or 'lockjaw' is an acute, usually fatal disease caused by a bacterium Clostridium tetani found in soil. |
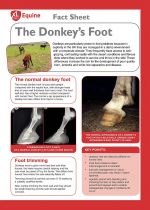 |
Donkeys are particularly prone to foot problems because in captivity in the UK they are managed in a damp environment with a temperate climate. They frequently have access to lush grazing, contrasting vastly with the desert conditions and fibrous diets where they evolved to survive and thrive in the wild. These differences increase the risk for the development of poor quality horn, laminitis and white line separation and disease. |
 |
The donkey is very stoical in nature, which can make detection of sickness and disease very difficult. Dullness and depression are frequently the only symptoms exhibited for a number of conditions, including severe and life threatening illness. Donkeys are affected by many of the same conditions as horses, but may present in a different way e.g. colic presenting as dullness only. Any dull donkey should be promptly examined by a vet to prevent development of hyperlipaemia, a potentially fatal condition. |
 |
A healthy foal will grow rapidly, gaining up to 90% of its adult height in the first two years of life. Getting a foal’s growth rate and development right during this time is essential for providing the foal with the best possible start for an athletic career.
There are many different factors that will affect a foal’s start in life, but the ones that we can control and manage include:
appropriate diet for age and stage of growth
de-worming
preventive vaccination program
farriery. |
 |
There are a number of contagious diseases which can affect our pets. These can cause severe illness or in many cases can be fatal. Many of the diseases are preventable by vaccination. This leaflet will help you understand what protection is available for your pet. |
 |
After eleven months of waiting, when your bundle of joy finally arrives; it is worth knowing some facts about the newborn foal, especially about the first few hours of life. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about the Oestrus cycle. |
 |
A rig is an entire male horse with no signs of external testicles so appears to be a gelding; but one or two testicles are still present, producing testosterone. A rig behaves like a stallion and, potentially, may be fertile. Their behaviour is unpredictable and they can be dangerous to handle so they should be castrated.
Some geldings still show stallion-like behaviour despite being fully castrated; they are called “false rigs”. The only form of treatment in these cases is behavioural therapy. |
 |
Together with fleas, ticks and mites are some of the most common parasites affecting our pets in the UK. This leaflet considers the threats posed to our pets by ticks and mites and how you might suspect that your pet is affected. Some of these external parasites also carry human health implications, which will be highlighted where relevant. |
 |
Dorsal displacement of the soft palate (DDSP) is a performance-limiting condition of the upper respiratory tract which occurs during fast exercise when the soft palate moves above the epiglottis (part of the larynx), creating a functional obstruction within the airway. This restricts airflow to the lungs and causes a sudden loss of performance and often a choking or gurgling noise. |
 |
A Tie-back and a Hobday are surgical procedures commonly performed together as treatment for recurrent laryngeal neuropathy (RLN), a condition causing paralysis of the nerve supplying the muscles of the larynx. This is the most common cause of abnormal respiratory noise in exercising horses and is often referred to as ‘whistling’ or ‘roaring’. It almost exclusively occurs in large horses, primarily Thoroughbreds and Warmbloods |
 |
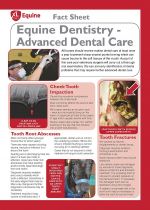
Dental problems such as tooth root abscesses, fractured teeth and periodontal disease will commonly require dental extraction as part of the treatment protocol.
Dental extraction can be a time consuming and difficult process (even when the teeth feel loose!) and requires a wide range of surgical equipment. Dental extraction should only be carried out by a veterinary surgeon with experience in dental surgery. |
 |
bTB is caused by Mycobacterium bovis, a bacteria that can infect many different animals. It is spread either by inhaling or consuming the bacteria and is usually associated with animals living in enclosed spaces. It can also be spread through contaminated surfaces such as feed troughs and pasture. The disease causes weight loss, coughing, fever, lethargy and ultimately, death. |
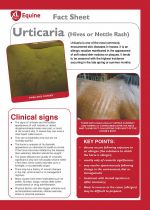 |
Urticaria is one of the most commonly encountered skin diseases in horses. It is an allergic reaction manifested in the appearance of soft raised skin nodules or plaques. |
 |
Vaccinations protect your horse against life-threatening diseases such as tetanus, and diseases that can severely affect their health and performance, such as equine influenza (flu). |
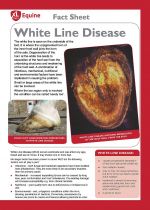 |
The white line is seen on the underside of the foot. It is where the unpigmented horn of the inner hoof wall joins the horn of the sole. |
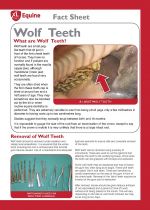 |
Wolf teeth are small peg-like teeth that sit just in front of the first cheek teeth of horses. |
 |
Why do we need to worm?
Worms in excessive numbers cause many gastrointestinal problems in horses, ponies and donkeys. A combination of pasture management, worm egg counts (WECs) and targeted worming will ensure that these worm burdens are kept to a healthy level and minimise the risk of disease. |
 |
There are a variety of different worms that can affect pets. The main worms that affect dogs and cats are roundworms and tapeworms which live in the intestine of your pet. Lung worm is also becoming increasingly common and occasionally we see infection with other types of worm such as hookworms and whipworms. |
 |
This leaflet is designed to help you understand how to monitor a wound, dressing or bandage at home. It will also help you understand when to contact the surgery for advice or re-examination. |
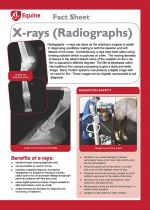 |
Radiographs - x-rays are taken by the veterinary surgeon to assist in diagnosing conditions relating to both the skeleton and soft tissue of the horse. |












































































































































































