 |
Coccidia are single celled protozoal organisms of the genus Eimeria. They have a complex life cycle involving both asexual and sexual reproduction. |
 |
Bovine Digital Dermatitis (BDD) is a common cause of infectious lameness worldwide. |
 |
It takes four to six months for the eggs in a cow's ovaries to grow to their ovulatory state. Management of the cow during this period is critical in determining their ability to yield transferable embryos that become established pregnancies. |
 |
Before pasteurisation of milk (1935) and compulsory testing
(1950) bovine TB (bTB) was a recognised cause of death in humans.
In cattle, emaciation due to lung disease was common. The testing
programme reduced the incidence of disease in cattle to very low
levels by the late 1970s, but there remained a persistent level of
disease in the South West. |
 |
Managing reproduction effectively to achieve optimum fertility is essential to the running of a profitable cattle enterprise. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about the BVD Virus. |
 |
Respiratory disease in calves is an interaction between the environment, the immunity of the calf and the various infectious agents involved. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about the Calf Scour. |
 |
Campylobacter foetus venerealis is one of the many potential causes of bovine infertility and abortions. It is transmitted from cow to bull to cow at serving. |
 |
Colostrum is the fuel of life and making sure your calves get enough is the cornerstone to all successful calf rearing enterprises. |
 |
Cryptosporidiosis is a disease caused by Cryptosporidium parvum (C. parvum)infection which is spread by contact with reservoir hosts, i.e. cattle, sheep and goats or the environment in which these are housed. |
 |
This factsheet looks at Dairy Cow Lameness. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about Dairy Herd Biosecurity. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about Environmental Mastitis. |
 |
Your ram is half the solution to getting a high percentage of ewes in lamb quickly to give a tight lambing period and help get lambs away early. He may also have cost a lot of money in the hope of
either improving the genetics of the flock or producing better lambs for sale. However, too often his ability to mate ewes and get them in lamb is taken for granted, often until it is too late and ewes are returning. A pre-breeding exam can rule out common problems and may indicate the need for collecting and testing a sample of semen to confirm fertility. |
 |
IBR is the most obvious clinical disease associated with infection by Bovine Herpesvirus 1 (BoHV-1). IBR is a disease of the upper respiratory tract which varies in severity, depending on the strain
of virus involved and other factors which may influence the immune status of the animal. In severe
cases, damage to the upper airways may lead to pneumonia and sometimes death. BoHV-1 infection has also been associated with infertility, abortion, high temperatures and milk drop. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about infertility problems in dairy herds. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about Johne's Disease. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about liver fluke in cattle. |
 |
The time immediately around calving (periparturient period) is the most critical part of a cow's year for many health and production reasons. |
 |
Perhaps the most common and significant neurological disorder, metabolic disease tends to affect adult sheep, particularly around lambing time. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about Milk Fever. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about how you can minimise calving difficulties. |
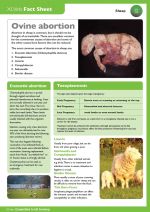 |
Abortion in sheep is common, but it should not be thought of as inevitable. There are excellent vaccines for the commonest causes of abortion and some of the other causes have factors that can be reduced. |
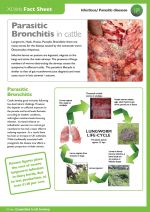 |
Lungworm, Husk, Hoose, Parasitic Bronchitis: there are many names for the disease caused by the nematode worm Dictyocaulus viviparous.
Infective larvae on pasture are ingested, migrate to the lungs and enter the main airways. The presence of large numbers of worms obstructing the airways causes the symptoms in affected cattle. The parasite’s lifecycle is similar to that of gut roundworms and most cases occur in late summer / autumn. |
 |
Schmallenberg virus was first detected in August 2011 within Germany, spreading to the Netherlands, Belgium and now the UK. |
 |
For many UK fl ocks, lameness is an endemic problem and prevalence has probably increased following the change in weather patterns to mild winters and wet summers. |
 |
British summer weather may be unpredictable but summer mastitis certainly isn't. It is a disease that changes little over the years, affecting the same farms year after year and often just certain fields within those holdings. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about teat health. |
 |
This factsheet provides details about the Oestrus cycle. |
 |
bTB is caused by Mycobacterium bovis, a bacteria that can infect many different animals. It is spread either by inhaling or consuming the bacteria and is usually associated with animals living in enclosed spaces. It can also be spread through contaminated surfaces such as feed troughs and pasture. The disease causes weight loss, coughing, fever, lethargy and ultimately, death. |






























